Loguytren problems, or Dupuytren’s contracture, cause tissue thickening in the palm, leading to finger curling and reduced mobility, making daily tasks like gripping objects difficult.
Early diagnosis is essential for effective management. Non-surgical options like physical therapy and enzyme injections can help, while severe cases may require surgical intervention such as needle aponeurotomy. Using assistive devices can also improve daily functioning and quality of life.
What Are Logistics Problems?
Loguytren problems, often referred to as Dupuytren’s contracture, involve a progressive condition affecting the hand. This condition results from the thickening of tissue in the palm.
This thickened tissue forms cords that can pull the fingers inward, leading to significant mobility issues. Typically, the ring and little fingers are most affected. The condition can develop slowly over time, often without noticeable symptoms initially.
Early Symptoms

The early symptoms of Loguytren problems include palm nodules. These nodules are small, hard lumps that can be felt in the palm. Initially, they may not cause pain but can contribute to finger stiffness over time.
Other early symptoms include tight cords forming beneath the skin. This tissue thickening is a primary indicator of the condition.
Progression of the Condition
As Loguytren’s problems progress, the nodules evolve into thick cords. These cords tighten over time, pulling the fingers closer to the palm. The condition can progress slowly, often taking years to develop.
However, in some cases, progression may be more rapid, especially in younger individuals. This can result in significant hand mobility issues and severe bending of the fingers.
Impact on Daily Life
Loguytren problems can greatly impact daily life. Individuals may struggle with holding objects or performing tasks that require full hand mobility. Simple tasks like shaking hands or opening jars can become frustrating.
The limitations in hand function can affect social interactions and self-esteem. Many people report a decrease in their overall quality of life due to these challenges.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a common condition that can coexist with Loguytren problems. It involves inflammation of the joints, leading to pain and stiffness.
In the hands, arthritis can exacerbate the difficulties caused by Loguytren problems. The combination of these conditions can severely limit hand function.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a specific type of arthritis commonly affecting the hands. It occurs due to the wear and tear of cartilage in the joints. Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
This condition can complicate the already challenging hand mobility issues associated with Loguytren problems.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
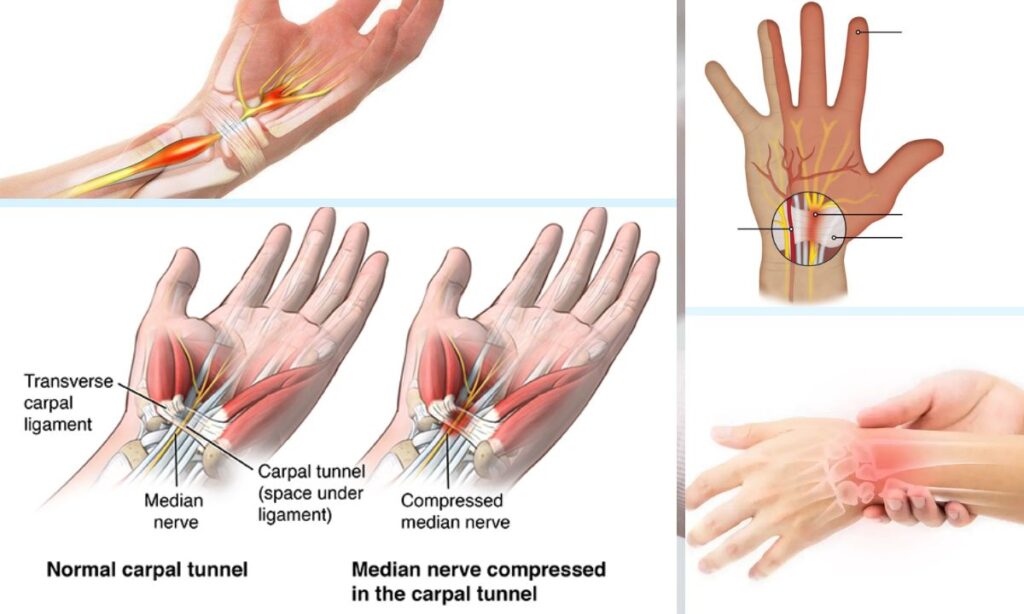
Carpal tunnel syndrome is another condition that can occur alongside Loguytren problems. It results from compression of the median nerve in the wrist.
Symptoms include tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand. The presence of carpal tunnel syndrome can further hinder hand function, making tasks more difficult.
Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts are fluid-filled lumps that can develop on the wrist or hand. While these cysts are usually benign, they can cause discomfort and limit hand mobility.
If they press on nerves, symptoms may include pain and weakness in the hand. Treatment may be necessary if the cysts interfere with daily activities.
Tendon Problems
Tendon problems, such as tendonitis, can also affect individuals with Loguytren problems. Inflammation of the tendons in the hand can lead to pain and reduced mobility.
This condition can complicate the already limited hand function, making it essential to address both issues simultaneously.
Causes and Risk Factors
Loguytren problems have several causes and risk factors. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as the condition often runs in families. Additionally, age and gender are important factors; it is more common in men over 40.
Lifestyle factors, such as smoking and alcohol consumption, can also increase the risk. Individuals with diabetes or seizure disorders may be more prone to developing this condition.
What to Do About It: Treatment and Management
Effective treatment and management are crucial for Loguytren problems. Early diagnosis by a hand specialist can lead to better outcomes. Consulting a medical professional can provide insight into the best treatment options available.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments can help manage symptoms and slow progression. Physical therapy is often recommended to improve hand flexibility. Stretching exercises can maintain movement in the fingers.
Enzyme injections, such as collagenase, can dissolve thickened cords. Steroid shots may reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief.
Surgical Treatments
For more severe cases, surgical procedures may be necessary. Needle aponeurotomy is a minimally invasive option that releases tight cords. Fasciectomy involves the removal of the thickened tissue to restore hand function.
Post-surgery recovery may include rehabilitation and physical exercises to regain strength and flexibility.
Living with Loguytren Problems: Coping Strategies

Living with Loguytren problems requires effective coping strategies. Using assistive devices can help individuals perform daily activities with greater ease.
Ergonomic tools are designed to reduce strain on the hands. Mental health support, including counseling, can aid in managing the emotional challenges associated with the condition.
Hand Practice Effects on Brain
Practicing hand movements can have positive effects on brain function. Engaging in hand exercises enhances brain plasticity.
This improvement strengthens neural connections related to motor control and coordination. Regular practice can help maintain fine motor skills and improve overall hand function.
What Causes Loss of Dexterity in Hands
Loss of dexterity in the hands can be caused by various conditions. Nerve compression, such as in carpal tunnel syndrome, can impede finger movement.
Tendon injuries can also lead to difficulty with fine motor skills. Arthritis can stiffen joints, reducing overall dexterity.
What Causes Loss of Strength in Both Hands
Loss of strength in both hands can result from multiple factors. Conditions like arthritis and tendonitis can weaken grip strength.
READ THIS BLOG:Look What Mom Found Giveaways: Your Ticket to Free Family Fun!
Neurological disorders may also contribute to muscle weakness. Lifestyle factors, such as inactivity, can lead to muscle atrophy, further diminishing hand strength.
10 Causes of Hand Weakness
Hand weakness can stem from several underlying conditions. Common causes include arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, Dupuytren’s contracture, and tendon injuries.
- Arthritis: inflammation of joints leading to pain and stiffness.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: compression of the median nerve in the wrist causing numbness and weakness.
- Dupuytren’s Contracture: Thickening of tissue in the palm that pulls fingers inward.
- Tendon Injuries: Damage or inflammation in tendons affecting movement and strength.
- Nerve Compression: Pressure on nerves that can lead to pain and weakness.
- Diabetes-Related Neuropathy: Nerve damage due to diabetes affecting hand function.
- Stroke: sudden loss of strength due to disrupted blood flow to the brain.
- Multiple Sclerosis: A neurological condition that can cause weakness and coordination issues.
- Thyroid Disorders: imbalances in thyroid hormones affecting muscle strength.
- Poor nutrition: deficiencies in essential nutrients impact overall muscle function.
Sudden Loss of Use of Right Hand
A sudden loss of use of the right hand is a serious concern. This could indicate a stroke, nerve injury, or acute trauma. Immediate medical evaluation is essential to determine the cause and initiate appropriate treatment.
Arthritis Pain in Hands and Fingers
Arthritis pain in the hands and fingers often presents as joint stiffness and swelling. Early signs may include pain during movement and tenderness in affected areas.
It is important to seek medical advice for effective management of arthritis symptoms.
What Are the First Signs of Arthritis in Fingers?
The first signs of arthritis in the fingers include joint pain and stiffness. Individuals may also notice swelling and a reduced range of motion. These early symptoms can signal the need for medical evaluation and intervention.
Losing Grip in Hands and Dropping Things
Losing grip strength and dropping objects is a common issue. This can result from conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or arthritis. Muscle weakness and nerve compression can make it difficult to hold onto items securely.
Frequently Asked Questions?
How to Stop Hand Tremors?
To stop hand tremors, consider reducing caffeine intake, managing stress through relaxation techniques, and consulting a healthcare professional for possible medications or therapies.
What Causes Sudden Weakness?
Sudden weakness can be caused by various factors, including neurological issues, dehydration, low blood sugar, or underlying medical conditions like anemia or heart problems.
What Are Three Warning Signs of Fatigue?
Three warning signs of fatigue include persistent tiredness despite adequate rest, difficulty concentrating or making decisions, and decreased motivation or energy levels throughout the day.
What Blood Tests Are Done for Weakness?
Blood tests for weakness may include a complete blood count (CBC) to check for anemia, thyroid function tests to assess hormonal imbalances, and metabolic panels to evaluate electrolyte levels.
Why Am I Suddenly Physically Weak?
Sudden physical weakness can result from acute illness, extreme fatigue, medication side effects, or serious conditions like stroke or heart attack, requiring prompt medical evaluation.
Conclusion
Loguytren problems, primarily characterized by Dupuytren’s contracture, can severely affect hand function and daily activities. The thickening of tissue in the palm leads to finger curling and mobility issues, impacting tasks that require fine motor skills.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for effective management. Treatment options range from non-surgical approaches, such as physical therapy and enzyme injections, to surgical procedures for more severe cases.
Living with this condition necessitates effective coping strategies and support. By addressing symptoms promptly, individuals can maintain hand function and improve their overall quality of life.

tina Morris is an experienced blogger and a passionate wordsmith at dofollowtips. With a keen eye for language and a deep love for writing, she shares insightful posts on grammar, phrases, and the art of communication.